Sugarcane is a significant cash crop in India, but its cultivation requires intensive labor, which is increasingly hard to find. Additionally, labor costs are high, making it challenging for farmers to cultivate sugarcane profitably. For example, preparing one hectare of land for sugarcane cultivation requires 25 workers for plowing, 50 for planting, and 60 for tasks like weeding, fertilizing, and irrigation. Harvesting, bundling, and loading onto trucks alone requires around 150 workers.
Due to the shortage of timely labor, farmers face delays and higher cultivation costs, reducing their yield and profits. This situation has led to farmers gradually reducing their sugarcane acreage every year.
To resolve these challenges, lower production costs, and increase profitability, the mechanization of sugarcane farming has become essential. Through mechanization, all major operations, from planting to harvesting, can be handled efficiently.
Importance of Mechanization
Mechanization in sugarcane farming can help reduce labor needs, cut costs, and improve yields. For this, some adjustments are necessary, such as increasing the row spacing from 90 cm to 120 or 160 cm, which allows machines to carry out tasks like planting, weeding, and fertilizing effectively.
Today, machines play a crucial role in sugarcane cultivation, categorized as follows:
- Land Preparation Machines
- Planting Machines
- Maintenance Machines
- Harvesting Machines
- Cover Crop Machines
Land Preparation Machines
- Chisel Plow: This plow helps break compacted soil layers up to 50 cm deep, improving root growth and water infiltration.
- Disc Plow: This tool overturns clods up to 40 cm deep, preparing the soil after harvest and incorporating stubble back into the soil.
- Tiller or Cultivator: Attached to a tractor, this tool crushes larger clods into fine particles and removes weeds, enhancing soil texture.
- Rotavator: Pulverizes soil into fine particles for planting, making it easier for roots to penetrate.
- Furrow Maker: Prepares rows for planting, allowing faster and more cost-effective preparation of the land.
- Pit Digger: Used for pit-planting sugarcane, digging pits 120 cm wide and 150 cm deep, allowing for up to 250 pits in an hour.
Planting Machines
- Set Cutter: Prepares single-bud setts for planting, which require less planting material and enhance yield.
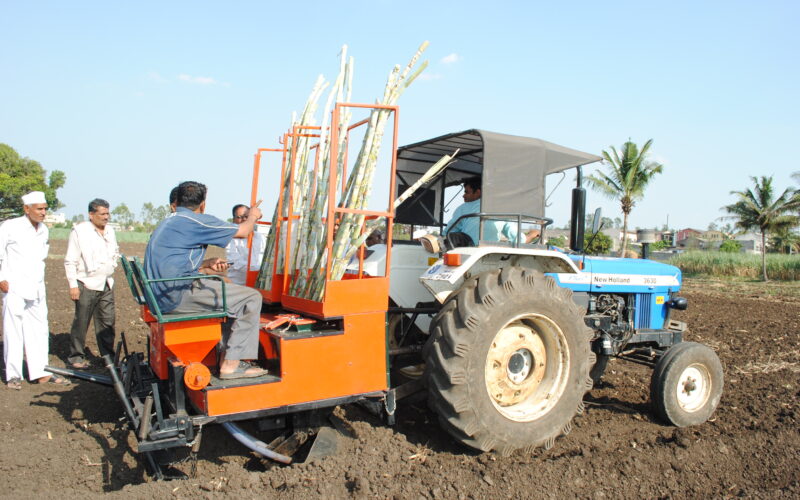
- Sugarcane Planter: This tractor-mounted machine performs multiple tasks, including row-making, cutting, fertilizing, and covering the seeds in one pass. It can plant about 1.2 hectares (3 acres) per day, reducing the labor requirement significantly.
Maintenance Machines
- Power Tiller: Useful for inter-row cultivation, weeding, and soil aeration.
- Mini Tractor: Ideal for narrower spacing, effectively manages soil and weeds between rows.
- Sprayer: Power tiller-mounted sprayers provide pest control and nutrient application, helping maintain plant health.
- Leaf Remover: Reduces labor required for removing dried leaves, which would otherwise demand significant manpower.
Harvesting Machines
- Kareep Harvester: Imported from the West Indies, this machine cuts sugarcane at ground level and can harvest 100 tons per day.
- Mini Harvester: Operates with a 60 HP tractor, capable of harvesting 50 tons per day.
- Astaf 7000 Harvester: Cuts sugarcane into 10-12 inch segments and processes up to 400 tons per day, making it suitable for large-scale harvesting.
Cover Crop Machines
- Shredder: Breaks down stubble into smaller pieces that decompose into the soil, adding nutrients.
- Stubble Cutter: Cuts stubble close to the ground, promoting the growth of cover crops.
Future Scope of Mechanization in Tamil Nadu
Currently, Tamil Nadu’s sugarcane farming relies on machines primarily for land preparation and weeding, while mechanized harvesting is limited. With labor availability expected to decrease further in the future, mechanization will become even more essential. The Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, sugar mill management, and agricultural departments are actively working to develop advanced harvesters suited for local conditions. With these advancements, mechanized sugarcane farming holds promise for a more profitable and sustainable future for farmers.
Dr. M. Shanmuganathan, Associate Professor, Department of Crop Breeding, Agricultural College and Research Institute, Kudumiyanmalai, Pudukkottai District.